
O 2 - Seven-pass erase, consisting of zero fills and all-ones fills plus a final random fill. Ownership of the affected disk is required. If you need to erase all contents of a partition but not its hosting whole-disk, use the zeroDisk or randomDisk verbs.

Erasing freespace on a volume will leave your files intact, indeed, from an end-user perspective, it will appear unchanged, with the exception that it will have attempted to make it impossible to recover deleted files. Secure erasing makes it harder to recover data using "file recovery" software.Įrasing a whole-disk will leave it useless until it is partitioned again.

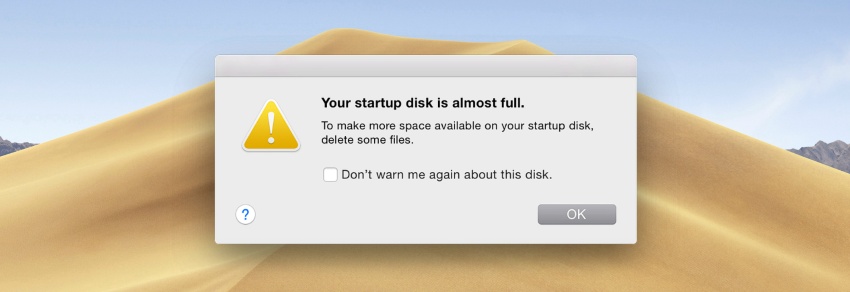
#Mac how to clear startup disk space free#
Within the man pages, you’ll find the explanation for how to securely erase a disk’s free space using diskutil: secureErase level deviceĮrase, using a "secure" (but see the NOTE below) method, either a whole-disk (including all of its partitions if partitioned), or, only the free space (not in use for files) on a currently-mounted volume. To find out about diskutil in detail, type man diskutil at the Terminal prompt. Proceed with caution, and make sure your backups are current before you try any of the following.) (Please note that, as with many Terminal commands, there’s a chance of Really Bad Things happening if you make a mistake with the following instructions. Selecting a region changes the language and/or content on if you want to do this from Terminal instead? In Terminal, a program named diskutil provides most of the features of macOS’s Disk Utility. Defragment drives with scratch disks regularly.RAID disks/disk arrays are good choices for dedicated scratch disk volumes.Scratch disks should be on a different drive than the one your operating system uses for virtual memory.Scratch disks should be on a different drive than any large files you are editing.In fact, using an SSD is probably better than using a separate hard disk as your primary scratch disk. An SSD, on the other hand, performs well as both the primary startup and scratch disk. If your startup disk is a hard disk, as opposed to a solid-state disk (SSD), try using a different hard disk for your primary scratch disk.Photoshop supports up to 64 exabytes of scratch disk space on up to four volumes. If you have more than one hard drive, you can specify additional scratch disks. To improve performance, set the scratch disk to a defragmented hard disk that has plenty of unused space and fast read/write speeds.The bandwidth limits for various ports are as follows: For best performance, connect the scratch disks to a compatible port that has the highest bandwidth limit of all the available ports.If you make large changes to dense pixel layers (that is, using several filters on complex background images or many edits to large smart objects) you could need as many times the size of the original file as there are history states.Additional free space may be required based on the file type you're working with. It is recommended to have minimum 20 GB of free space on your OS hard drive while working with Photoshop. If you make small changes only, you need a minimum of 10 GB scratch disk space for Photoshop (with default preferences, brushes, patterns, etc).So, if the free space in your scratch disk is 10 GB, available space that Photoshop will consider in the scratch disk is 10 - 6 = 4 GB, which may/may not be enough for the current operation being performed. However, this is the minimum space that Photoshop tries to keep free in the scratch disk, and the available space that Photoshop considers in a scratch disk is the 6 GB subtracted from the current free space in the disk. Minimum free space on a scratch disk should be 6 GB for Photoshop desktop.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
